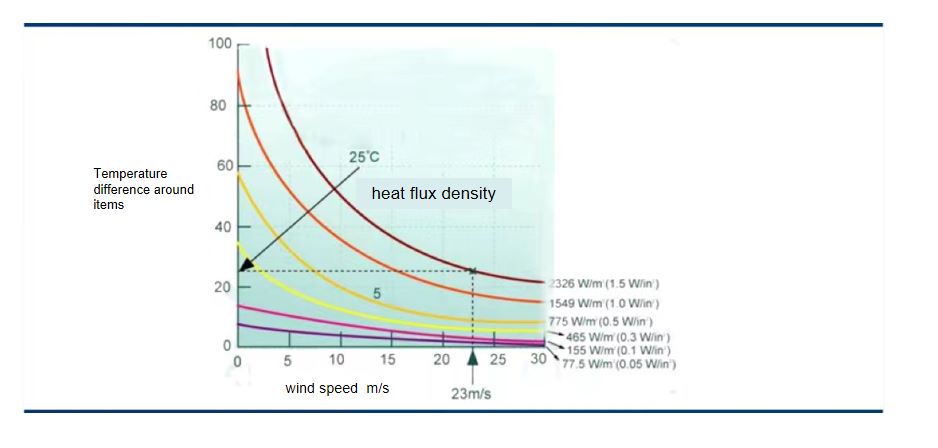
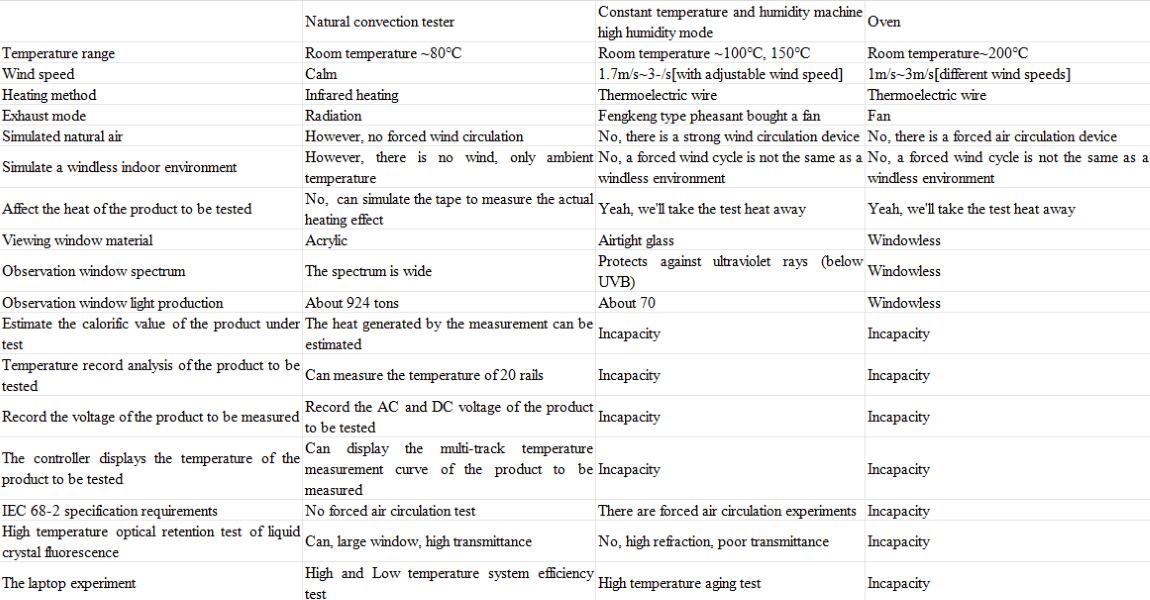
Comparison of Climatic Test and Environmental Test
Climate environment test -- constant temperature and humidity test chamber, high and low temperature test chamber, cold and hot shock test chamber, wet and heat alternating test chamber, rapid temperature change test chamber, linear temperature change test chamber, walk-in constant temperature and humidity test chamber, etc. They all involve temperature control.

Because there are multiple temperature control points to choose from, the climate chamber temperature control method also has three solutions: inlet temperature control, product temperature control and "cascade" temperature control. The first two are single-point temperature control, and the third is two-parameter temperature control.
Single point temperature control method has been very mature and widely used.
Most of the early control methods were "ping-pong" switch control, commonly known as heating when it's cold and cooling when it's hot. This control mode is a feedback control mode. When the temperature of the circulating air flow is higher than the set temperature, the electromagnetic valve of refrigeration is opened to deliver cold volume to the circulating air flow and reduce the temperature of the air flow. Otherwise, the circuit switch of the heating device is switched on to directly heat the circulating air flow. Raise the temperature of the air stream. This control mode requires that the refrigeration device and heating components of the test chamber are always in a standby working state, which not only wastes a lot of energy, but also the controlled parameter (temperature) is always in an "oscillation" state, and the control accuracy is not high.
Now the single-point temperature control method is mostly changed to the universal proportional differential integral (PID) control method, which can give the controlled temperature correction according to the past change of the controlled parameter (integral control) and the change trend (differential control), which not only saves energy, but also the "oscillation" amplitude is small and the control accuracy is high.
Dual-parameter temperature control is to collect the temperature value of the air inlet of the test chamber and the temperature value near the product at the same time. The air inlet of the test chamber is very close to the installation position of the evaporator and heater in the air modulation room, and its magnitude directly reflects the air modulation result. Using this temperature value as the feedback control parameter has the advantage of quickly modulating the status parameters of the circulating air.
The temperature value near the product indicates the real temperature environmental conditions suffered by the product, which is the requirement of the environmental test specification. Using this temperature value as the parameter of feedback control can ensure the effectiveness and credibility of the temperature environmental test, so this approach takes into account the advantages of both and the requirements of the actual test. The dual-parameter temperature control strategy can be the independent "time-sharing control" of the two groups of temperature data, or the weighted two temperature values can be combined into one temperature value as a feedback control signal according to a certain weighting coefficient, and the value of the weighting coefficient is related to the size of the test chamber, the wind speed of the circulating air flow, the size of the temperature change rate, the heat output of the product work and other parameters.
Because heat transfer is a complex dynamic physical process, and is greatly affected by the atmospheric environment conditions around the test chamber, the working state of the tested sample itself, and the complexity of the structure, it is difficult to establish a perfect mathematical model for the temperature and humidity control of the test chamber. In order to improve the stability and accuracy of control, fuzzy logic control theory and method are introduced in the control of some temperature test chambers. In the control process, the thinking mode of human is simulated, and the predictive control is adopted to control the temperature and humidity space field more quickly.
Compared with the temperature, the selection of humidity measurement and control points is relatively simple. During the circulation flow of the well-regulated humid air into the high and low temperature cycle test chamber, the exchange of water molecules between the wet air and the test piece and the four walls of the test chamber is very small. As long as the temperature of the circulating air is stable, the circulating air flow from entering the test chamber to exiting the test chamber is in the process. The moisture content of wet air changes very little. Therefore, the relative humidity value of the detected air at any point of the circulating air flow field in the test box, such as the inlet, the middle stream of the flow field or the return air outlet, is basically the same. Because of this, in many test chambers that use the wet and dry bulb method to measure humidity, the wet and dry bulb sensor is installed at the return air outlet of the test chamber. Moreover, from the structural design of the test box and the convenience of maintenance in use, the wet and dry bulb sensor used for relative humidity measurement and control is placed at the return air inlet for easy installation, and also helps to regularly replace the wet bulb gauze and clean the temperature sensing head of the resistance PT100, and according to the requirements of the GJB150.9A wet heat test 6.1.3. The wind speed passing through the wet-bulb sensor should not be lower than 4.6m/s. The wet-bulb sensor with a small fan is installed at the return air outlet for easier maintenance and use.