Application of TCT Temperature Cycle Chamber in Optical Communication Industry
The arrival of 5G makes people feel the rapid development of mobile Internet, and optical communication technology as an important basis has also been developed. At present, China has built the world's longest optical fiber network, and with the continuous advancement of 5G technology, optical communication technology will be more widely used. The development of optical communication technology not only allows people to enjoy faster network speed, but also brings more opportunities and challenges. For example, new applications such as cloud gaming, VR, and AR require more stable and high-speed networks, and optical communication technology can meet these needs. At the same time, optical communication technology has also brought more innovation opportunities, such as intelligent medical care, intelligent manufacturing and other fields, will use optical communication technology to achieve more efficient and accurate operation. But you know what? This amazing technology cannot be achieved without the credit of macro environmental test equipment, especially the TC temperature cycle test chamber, which is a rapid temperature change test chamber. This article introduces you to the optical communication product reliability test quality manager - rapid temperature change laboratory.

First, let's talk briefly about optical communication. Some people also say that it is called optical communication, so they are two in the end is not a concept. In fact, they are two of the same concept. Optical communication is the use of optical signals for communication technology, and optical communication is based on optical communication, through optical devices such as optical fibers, optical cables to achieve data transmission. Optical communication technology is widely used, such as our daily use of fiber optic broadband, mobile phone optical sensors, optical measurement in aerospace and so on. It can be said that optical communication has become an important part of modern communication field. So why is optical communication so popular? In fact, it has many advantages, such as high-speed transmission, large bandwidth, low loss and so on.
Common optical communication products include: optical cable, fiber switch, fiber modem, etc., used to transmit and receive optical signals of optical fiber communication equipment; Temperature sensor, strain sensor, displacement sensor, etc., can measure various physical quantities in real time and other optical fiber sensors; Erbium-doped optical amplifier, erbium-doped ytterbium-doped optical amplifier, Raman amplifier, etc., used to expand the intensity of optical signals and other optical amplifiers; Helium-neon laser, diode laser, fiber laser, etc., are light sources in optical communication, used to produce high brightness, directional and coherent laser light and other lasers; Photodetectors, optical limiter, photodiodes, etc., for receiving optical signals and converting them into electrical signals and other optical receivers; Optical switches, optical modulators, programmable optical arrays, etc. are used to control and adjust optical signal transmission and routing and other optical controllers. Let's take mobile phones as an example and talk about the application of optical communication products on mobile phones:
1. Optical fiber: Optical fiber is generally used as a part of the communication line, due to its fast transmission speed, communication signals are not easily affected by external interference and other characteristics, has become an important part of mobile phone communication.
2. Photoelectric converter/optical module: photoelectric converter and optical module are devices that convert optical signals into electrical signals, and are also a very important part of mobile phone communication. In the era of high-speed communication such as 4G and 5G, the speed and performance of such equipment need to be continuously improved to meet the needs of fast and stable communication.
3. Camera module: In the mobile phone, the camera module generally includes CCD, CMOS, optical lens and other parts, and its quality and performance also have a significant impact on the quality of optical communication of the mobile phone.
4. Display: Mobile phone displays generally use OLED, AMOLED and other technologies, the principle of these technologies are related to optics, but also an important part of mobile phone optical communication.
5. Light sensor: Light sensor is mainly used in mobile phones for environmental light sensing, proximity sensing and gesture sensing, and is also an important mobile phone optical communication product.
It can be said that optical communication products fill all aspects of our life and work. However, the production and use environment of optical communication products is often changeable, such as high or low temperature weather environment when working outdoors, or the use of a long time will also encounter changes in thermal expansion and contraction. So how is the reliable use of these products achieved? That has to mention our protagonist today - rapid temperature change test chamber, also known as TC box in the optical communication industry. In order to ensure that optical communication products still work normally under various environmental conditions, it is necessary to carry out rapid temperature change tests on optical communication products. The rapid temperature change test chamber can simulate a variety of different temperature and humidity environments, and simulate instantaneous extreme environmental changes in the real world within a rapid range. So how is the rapid temperature change test chamber applied in the optical communication industry?
1. Optical module performance test: Optical module is a key component of optical communication, such as optical transceiver, optical amplifier, optical switch, etc. The rapid temperature change test chamber can simulate different temperature environments and test the performance of the optical module at different temperatures to evaluate its adaptability and reliability.
2. Reliability test of optical devices: optical devices include optical fibers, optical sensors, grating, photonic crystals, photodiodes, etc. The rapid temperature change test chamber can test the temperature change of these optical devices and evaluate their reliability and life based on the test results.
3. Optical communication system simulation test: The rapid temperature change test chamber can simulate various environmental conditions in the optical communication system, such as temperature, humidity, vibration, etc., to test the performance, reliability and stability of the entire system.
4. Technology research and development: The optical communication industry is a technology-intensive industry, which needs to constantly develop new technologies and new products. The rapid temperature change test chamber can be used to test the performance and reliability of new products, helping to accelerate the development and market of new products.
In summary, it can be seen that in the optical communication industry, the rapid temperature change test chamber is usually used to test the performance and reliability of optical modules and optical devices. Then when we use the rapid temperature change test chamber for testing, different optical communication products may require different standards. The following are rapid temperature change test standards for some common optical communication products:
1. Optical fiber: Common test standards There are common optical fiber rapid temperature change test standards are the following: IEC 61300-2-22: The standard defines the stability and durability test method of optical fiber components, section 4.3 of which specifies the thermal stability test method of optical fiber components, in the case of rapid temperature changes to the optical fiber components for measurement and evaluation. GR-326-CORE: This standard specifies reliability test requirements for fiber optic connectors and adapters, including thermal stability tests to assess the reliability of fiber optic connectors and adapters in temperature changing environments. GR-468-CORE: This standard defines the performance specifications and test methods for fiber optic connectors, including temperature cycle testing, accelerated aging testing, etc., to verify the reliability and stability of fiber optic connectors under various environmental conditions. ASTM F2181: This standard defines a method for fiber failure testing under high temperature and high humidity environmental conditions to evaluate the long-term durability of the fiber. And the above standards such as GB/T 2423.22-2012 are tested and evaluated for the reliability of optical fiber in rapid temperature changes or long-term high temperature and high humidity environments, which can help the majority of manufacturers to ensure the quality and reliability of optical fiber products.
2. Photoelectric converter/optical module: The common rapid temperature change test standards are GB/T 2423.22-2012, GR-468-CORE, EIA/TIA-455-14 and IEEE 802.3. These standards mainly cover the test methods and specific implementation steps of photoelectric converters/optical modules, which can ensure the performance and reliability of products in different temperature environments. Among them, the GR-468-CORE standard is specifically for the reliability requirements of optical converters and optical modules, including temperature cycle test, wet heat test and other environmental tests, requiring optical converters and optical modules to maintain stable and reliable performance in long-term use.
3. Optical sensor: The common rapid temperature change test standards are GB/T 27726-2011, IEC 61300-2-43 and IEC 61300-2-6. These standards mainly cover the test methods and specific implementation steps of the temperature change test of the optical sensor, which can ensure the performance and reliability of the product in different temperature environments. Among them, the GB/T 27726-2011 standard is the standard for the performance test method of optical sensors in China, including the environmental test method of optical fiber sensors, which requires the optical sensor to maintain stable performance in a variety of working environments. IEC 60749-15 standard is the international standard for the temperature cycle test of electronic components, and it also has reference value for the rapid temperature change test of optical sensors.
4. Laser: Common rapid temperature change test standards are GB/T 2423.22-2012 "Electrical and electronic products environmental test Part 2: Test Nb: temperature cycle test", GB/T 2423.38-2002 "Basic test methods for electrical components Part 38: Temperature resistance test (IEC 60068-2-2), GB/T 13979-2009 "Laser product Performance test method", IEC 60825-1, IEC/TR 61282-10 and other standards mainly cover the laser temperature change test method and specific implementation steps. It can ensure the performance and reliability of products in different temperature environments. Among them, the GB/T 13979-2009 standard is the standard for the performance test method of laser products in China, including the environmental test method of the laser under temperature changes, requiring the laser to maintain stable performance in a variety of working environments. The IEC 60825-1 standard is a specification for the integrity of laser products, and there are also relevant provisions for the rapid temperature change test of lasers. In addition, the IEC/TR 61282-10 standard is one of the guidelines for the design of optical fiber communication systems, which includes methods for the environmental protection of lasers.
5. Optical controller: The common fast temperature change test standards are GR-1209-CORE and GR-1221-CORE. GR-1209-CORE is a reliability standard for optical fiber equipment, mainly for the reliability test of optical connections, and specifies the reliability experiment of optical connection systems. Among them, the rapid temperature cycle (FTC) is one of the test projects, which is to test the reliability of optical fiber modules under rapidly changing temperature conditions. During the test, the optical controller needs to perform temperature cycling in the range of -40 ° C to 85 ° C. During the temperature cycle, the module should maintain normal function and not produce abnormal output, and the test time is 100 temperature cycles. GR-1221-CORE is a reliability standard for fiber optic passive devices and is suitable for the testing of passive devices. Among them, the temperature cycle test is one of the test items, which also requires the optical controller to be tested in the range of -40 ° C to 85 ° C, and the test time is 100 cycles. Both of these standards specify the reliability test of the optical controller in the environment of temperature change, which can determine the stability and reliability of the optical controller under harsh environmental conditions.
In general, different rapid temperature change test standards may focus on different test parameters and test methods, it is recommended to choose the corresponding test standards according to the use of specific products.
Recently, when we discuss the reliability verification of optical modules, there is a contradictory indicator, the number of temperature cycles of optical module verification, there are 10 times, and 20 times, 100 times, or even 500 times.
Frequency definitions in two industry standards:
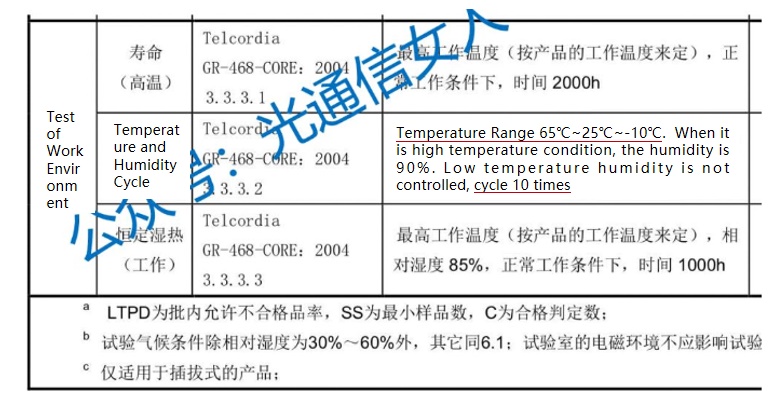
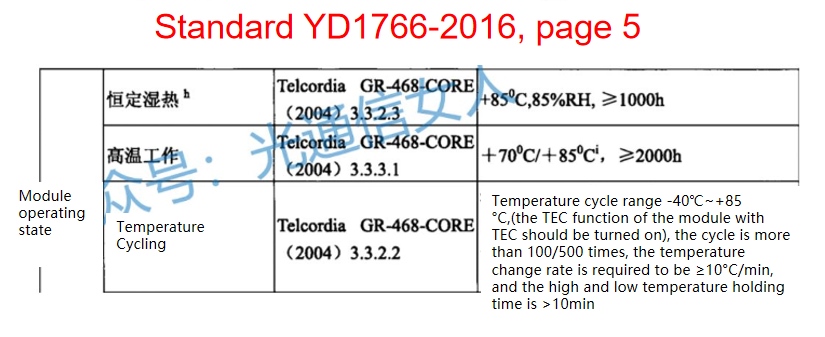
The references to these standards have clear sources and are correct.
For the 5G forward optical module, our opinion is that the number of cycles is 500, and the temperature is set at -40 °C ~85 °C
The following is the description of the 10/20/100/500 above in the original text of GR-468(2004)

Because of the limited space, this article introduces the use of rapid temperature change test chamber in the optical communication industry. If you have any questions when using rapid temperature change test chamber and other environmental test equipment, welcome to discuss with us and learn together.