The processes of cotton knitting fabric(scouring, bleaching , dyeing and etc.) is generally carried out in the overflow machine. During the entire processing, the fabric remains in a rope-like state. The fibers constantly bend and deform in the dyeing machine, the original hydrogen bonds are constantly broken while new hydrogen bonds are constantly formed. Sometimes the newly formed hydrogen bonds cannot be fully restored, thus forming chicken claw marks and dead creases on the fabric surface.
In the single-sided fabric structure, tension of the two sides of yarn is asymmetric. After fabric is folded in one direction for a long time, it is difficult to recover. Therefore, among various structures, especially on fabrics with less or larger weight (eg. plain weave and sweatshirt fabrics) are more prone to crease problems. The generation of creases is also closely related to yarn count and twist. The finer the yarn count and the higher the twist, the greater the possible reversal and untying of the yarn, and the more likely it is to cause crease problems.

The main process steps leading to creases: scouring and bleaching
1. The general dyeing and finishing process typically involves: fabric preparation → seam sealing → boiling and bleaching in the fabric dyeing machine → dyeing → soaping → color fixing → softening → fabric out from dyeing machine → dehydration → drying. It is commonly believed that creases mainly form in the dyeing machine. However, after rigorous experimental verification by our engineers, it has been found that most cotton knits actually develop creases during the boiling and bleaching stage, which are just not easily observable before dyeing.
2. Based on the years of experience of our engineers, the following types of fabric and equipments are prone to developing creases during the boiling and bleaching stage:
Fabric factors: Single-sided cotton fabrics with lighter or heavier weights (e.g., weights <150g or >300g), especially cotton spandex (with elastane) fabrics.
Machine factors: Compared to L-shaped overflow fabric dyeing machine, J-shaped overflow fabric dyeing machine are more prone to creating creases due to their stronger stretching force. Air-jet fabric dyeing machine, on the other hand, are less likely to cause creases because the fabric is fully blown open by high-pressure air at the nozzles, allowing the fibers to "rest" from tension, which aids in eliminating internal stress and reducing creasing issues.
Process factors: Fabrics that have not undergone prestretching are more prone to creasing. Fixing the fabric under high temperatures can improve fiber proximity and orientation, stabilize fiber morphology and reduce likelihood of changes occurring in dyeing machine, which is beneficial for reducing creases.

350g pure cotton knitted fabric (no creases after dyeing)

140g pure cotton knitted jersey (no creases after dyeing)
Solutions of scouring and belaching creases
1. General Method: During boiling and bleaching, as well as dyeing, polyacrylamide-based lubricants are added. The primary role of this type of lubricating agent is to "reduce friction between fabrics and between fabrics and machinery," but it is difficult to resolve creases formed during boiling and bleaching.
2. Solution Proposed in This Article: To improve creases during boiling and bleaching, the following auxiliaries, processes, and operations are employed. Satisfactory results have been confirmed through applications by multiple clients.
Auxiliaries:
A. Preferentially select a high-concentration and highly soluble polyacrylamide-based anti-crease agent JET (non-ionic) for use in the bath. Its role is to reduce friction between fabrics and between fabrics and machinery.
B. Select new type of anti-crease softener RCE (non-ionic). Its role is to impart good softness and smoothness to the fabric itself, as well as to provide level dyeing properties.
The combined use of these two auxiliaries is the core of this method.
Process:
Reduce the heating rate; the focus is on reducing the cooling rate, with an optimal range of 1.0 to 1.5°C/min.
Operations:
Before entering the dyeing machine, the gray fabric should be placed in an area with high humidity in workshop to allow for sufficient moisture regain. During moisture regain, the fibers undergo some swelling, and internal stresses are partially eliminated, which is conducive to reducing creases. After the gray fabric is loosened, it should be allowed to freely pass through a J-shaped trough, while simultaneously being pressed by a press roll or stretched by rollers, which is conducive to eliminating internal stresses and reducing creases.
3.Process example
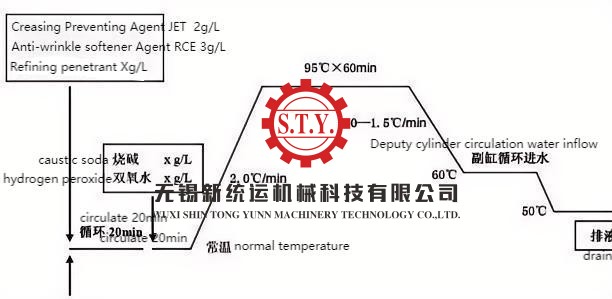
Before boiling and bleaching, add refining permeant, etc., anti-wrinkle agent JET and anti-wrinkle softening agent RCE in the bath, do not heating firstly, cycle for 20 minutes after entering the cloth, so that the grey cloth is fully moistened and the auxiliary agent fully reacts with the fabric fiber. If bleaching is required, caustic soda and hydrogen peroxide can be added before heating. Reduce the rate of heating; Especially to reduce the cooling rate, generally 1.0 ~ 1.5℃/min is better; And it must be completely cooled to 50 ° C to discharge the liquid for dyeing.
Other items to prevent creases
1. In order to prevent the generation of creases, it is recommended to add polyacrylamide type lubricant - JET in the bath during dyeing, and reduce the cooling rate.
2. When dehydrating and dry cloth, open width rolling water dry cloth can be used, which not only improves the efficiency of dry cloth, but also helps to solve the problem of creasing.
3. When stacking cloth, it is recommended that the weight should not be too large and the time should not be too long, especially when the wet cloth is stored.
4. If it is cotton rack (with spandex) fabric using this solution can not completely solve the crease problem, you can consider the presetting process.
5. Generally, the slight crease can be solved by the setting machine, and the stubborn can be returned to the cylinder washing water, gradually heating up to 85 ° C, gradually cooling down to 50 ° C process test repair, or can be re-shaped by steam in the industrial drying machine, which can be repaired according to their respective equipment and crease conditions.