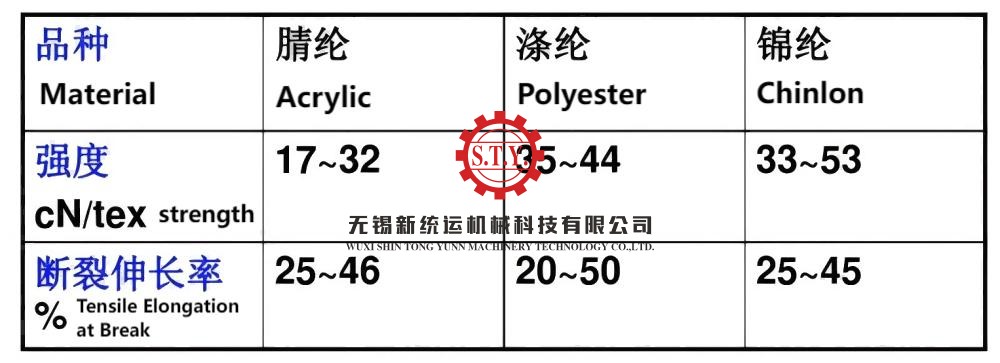
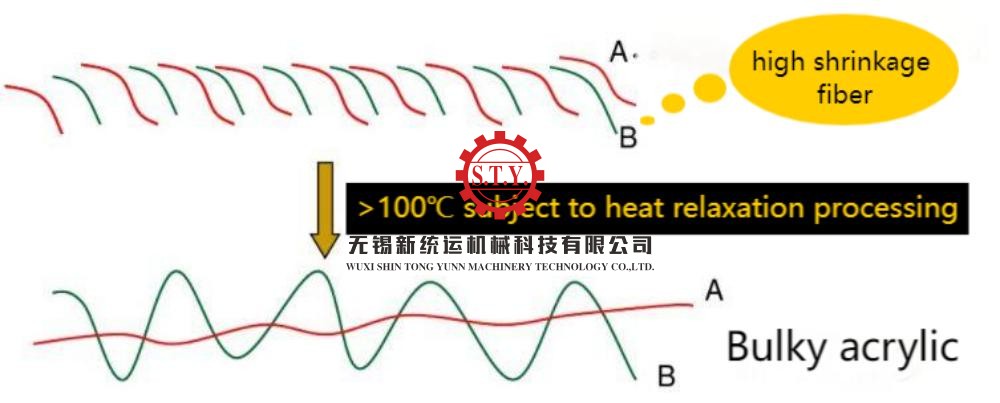
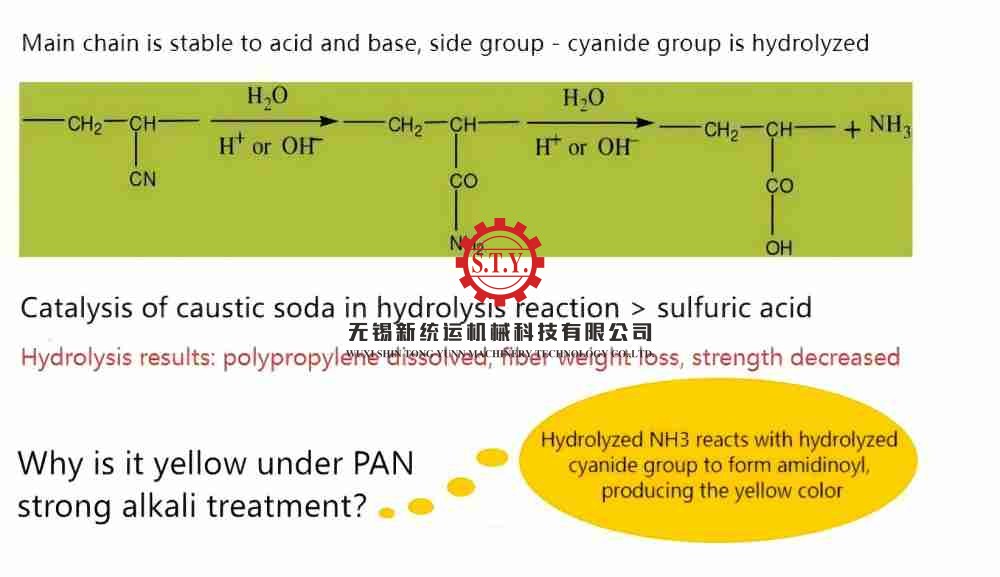
Textile dyeing machines are industrial equipment designed for the dyeing or coloring process of textiles. Dyeing is a critical step in the textile manufacturing industry, where dyes are applied to fabrics, yarns, or fibers to achieve the desired color or pattern.
I. Market Research
1. Market Size and Growth Trends
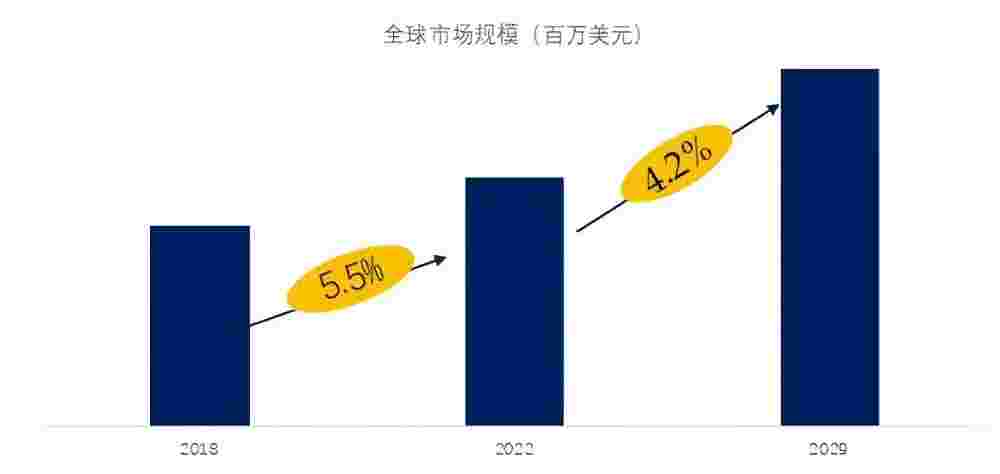
According to the latest report by QYResearch, “Global Textile Dyeing Machine Market Report 2023-2029,” it is expected that the global textile dyeing machine market will reach $1.37 billion by 2029, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.2% in the coming years. This indicates that the textile dyeing machine market will experience steady growth over the next few years.
2. Development Trends
Digitalization and Automation: With the continuous development of artificial intelligence, big data and other technologies, the textile dyeing machine industry is gradually moving towards digitalization and automation. The application of intelligent equipment not only improves production efficiency but also reduces production costs and enhances product quality.
Environmental Sustainability: With the increasing global awareness of environmental protection, eco-friendly solutions have become a mainstream trend in the textile dyeing machine industry. Major companies are adopting environmentally friendly production technologies and materials to achieve sustainable development.
Customization and Personalization: As consumer demand becomes more diverse, personalized and customized textile products are increasingly favored. Textile dyeing machine companies need to offer a variety of products and services to meet consumers' individual needs.

*knitted fabric dyeing machine
3.Potential Growth Drivers
Sustained Market Demand: With the global economic recovery and the improvement in consumer purchasing power, the demand for textiles continues to rise, providing significant growth opportunities for the textile dyeing machine market.
Emerging Markets: Emerging markets in Southeast Asia, Africa, and other regions offer vast growth potential for the textile dyeing machine industry.
Technological Innovations: New dyeing technologies such as digital dyeing and smart dyeing are constantly emerging, bringing new development opportunities to the textile dyeing machine market.
4. Potential Challenges
Environmental Pressure: With the tightening of environmental regulations, textile dyeing machine companies need to increase investments in environmental protection and improve the eco-friendliness of their products.
International Trade Barriers: Green trade barriers are becoming a significant factor limiting textile exports, requiring the textile dyeing machine industry to focus on green production.
Intense Market Competition: The domestic and international markets are highly competitive, requiring textile dyeing machine companies to continuously improve product quality and technological capabilities to stay ahead of the competition.
II. Industry Competitor Analysis
1. Major Manufacturers
Globally, leading manufacturers of textile dyeing machines include COSMOTEX, Gargo Corporation, Sclavos, Texfab, Thies, Chemtax, M/s Exolloys Engineering, Capto, and Loris Bellini. The top three companies account for approximately 54.9% of the market share.
2. Strategic Positioning and Competitive Advantages
Large Multinational Companies: These companies typically possess strong R&D capabilities and advanced technological expertise, allowing them to produce high-end, intelligent dyeing machines. They enjoy significant global market share and brand recognition. These companies focus on technological innovation and product quality, continuously introducing advanced dyeing machine models that meet market demands.
Small and Medium-Sized Local Enterprises: Compared to large multinational companies, small and medium-sized local enterprises also occupy a certain share of the textile dyeing machine market. They typically serve local markets by offering flexible production methods and personalized services.
3. Competitive Disadvantages
Some small and medium-sized enterprises lack sufficient investment in R&D and product innovation, resulting in weaker product competitiveness.
Some companies lack an international perspective and brand influence, making it difficult to secure a dominant position in the global market.

*small capacity fabric dyeing machine
III. Supply Chain Structure Analysis
1. Supply Chain Efficiency
The textile dyeing machine industry’s supply chain includes raw material suppliers, component manufacturers, machine manufacturers, distributors, and end users. Currently, there is a high degree of collaboration and coordination between different supply chain stages, leading to overall high efficiency.
2. Potential Bottlenecks
Raw Material Supply: The supply of some critical raw materials may be affected by market fluctuations, trade policies, and other factors, potentially leading to bottlenecks in the supply chain.
Technological Innovation: Technological innovation is a key driver of industry development, but some enterprises' insufficient investment in R&D may slow the overall improvement of supply chain technology.
IV. R&D Progress and Technological Innovation
1. New Dyeing Technologies
Emerging technologies such as digital dyeing and smart dyeing are creating new opportunities for the textile dyeing machine industry. These technologies not only improve dyeing efficiency and product quality but also reduce energy consumption and pollutant emissions.
2. Intelligent Production Lines
Intelligent production lines are an important development direction for the textile dyeing machine industry. By integrating smart equipment, companies can automate and optimize the production process, leveraging big data and cloud computing technologies to enable real-time analysis and processing of production data, thus improving production efficiency and product quality.
3. Application of New Materials
The development and application of new materials, such as functional fibers, smart fibers, and eco-friendly fibers, provide more possibilities for the textile dyeing machine industry, driving innovation and development.

*hank yarn spray dyeing machine
V. Regulatory and Policy Environment Analysis
1. Environmental Regulations
With increasing global environmental awareness, governments worldwide are strengthening the formulation and enforcement of environmental regulations. Textile dyeing machine companies must comply with these regulations, increasing their environmental investments and improving the eco-friendliness of their products.
2. Industrial Policies
During the “14th Five-Year Plan” period, national policies are placing higher demands on ecological civilization construction. The "3060" carbon neutrality goal will push the printing and dyeing industry to adopt more proactive and practical measures, such as technological innovation and pollutant control, to improve energy and resource efficiency, reduce pollutants, and achieve a balance between economic, ecological, and social benefits.
3. International Trade Policies
The rise of international trade protectionism and green trade barriers has impacted the export of textile dyeing machines. Companies need to closely monitor changes in international trade policies, strengthen international trade cooperation, and improve their products' international competitiveness.

The textile dyeing machine industry is expected to maintain steady growth in the coming years. However, it also faces many challenges. Companies need to continually enhance their technological innovation capabilities and product quality, adapt to changes in market demand, expand their market share and achieve sustainable development.